Video production has seen remarkable leaps in recent years, but perhaps none more transformative than the arrival of AI-driven visual effects (VFX). By analyzing massive datasets and learning from existing footage, AI algorithms can automate or drastically speed up tasks like color grading, rotoscoping, object removal, and even generating entirely new visuals. This convergence of machine learning and cinematic artistry opens the door to films, commercials, and social media content that push boundaries while saving creators time and money.
However, with these advanced tools come ethical concerns—deepfake videos, potential IP violations, and the blurred lines between reality and fiction. In this post, we’ll explore how AI-enhanced VFX works, the opportunities it brings to video production, and the guidelines creators should follow to maintain authenticity and trust.
From Traditional VFX to AI-Driven Workflows
Visual effects once relied on time-intensive manual work, but AI VFX is changing that narrative.
AI tools can now automate complex VFX processes—such as scene composition, background replacement, and motion tracking—cutting production time while increasing precision. This shift allows artists to focus more on creativity rather than repetitive tasks.
Traditional VFX
Historically, tasks like rotoscoping (manually tracing over footage), 3D modeling, and color correction consumed a huge chunk of post-production hours. Artists had to apply painstaking frame-by-frame edits, leaving minimal bandwidth for creative experimentation.
Machine Learning to the Rescue
Modern AI algorithms can “learn” the parameters of an effect or style from a reference set. Once trained, these models can automatically apply the style across an entire video sequence or even generate new frames with minimal human intervention.
Integration with Current Tools
Companies like Adobe, Blackmagic Design, and Autodesk are embedding AI features into their existing video-editing suites. This synergy allows editors and VFX artists to combine traditional manual precision with the efficiency of machine learning.
For a more general look at how AI is reshaping marketing, check out How AI Is Revolutionizing Digital Marketing.
2. AI-Enhanced VFX Techniques and Tools
AI is revolutionizing VFX workflows with intelligent automation and creative enhancement.
From AI-based rotoscoping that accurately isolates subjects to deep learning algorithms that predict lighting and shadows, these innovations accelerate production without compromising quality. Tools like Runway ML and NVIDIA Omniverse are leading the way, enabling faster, smarter, and more dynamic visuals.
1. Automated Color Grading
AI-driven color grading analyzes each frame to balance and enhance tones, minimizing the need for manual color correction. This can help match a specific cinematic style or maintain consistent lighting across varied shooting conditions.
2, Intelligent Rotoscoping and Object Removal
Instead of manually tracing around characters or objects, AI models detect edges and movement, accurately isolating elements for compositing or removal. This can drastically cut down on post-production time for complex scenes.
3. Style Transfer and Content-Aware Fills
AI can learn a visual “style” from a reference painting, film, or dataset, then apply it to new footage. Content-aware fills use predictive modeling to seamlessly fill gaps in the background when an object is removed or repositioned.
4, Deepfake-Style Facial Replacement
Though controversial, deepfake technology can be used responsibly to de-age actors, replace faces for stunts, or localize content with different actors without reshoots. However, it’s critical to maintain ethical guidelines and secure permissions.
Learn how these AI-enhanced techniques fit into broader video strategies in Lights, Camera, Conversion: Creating Videos That Drive Results
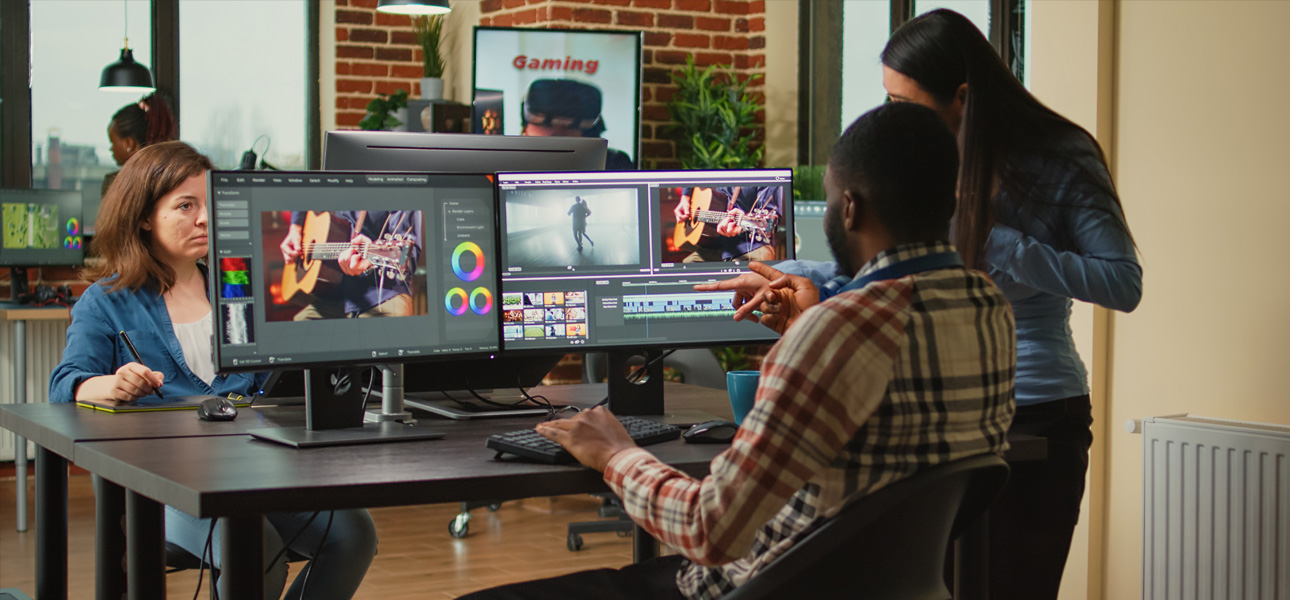

Advantages of AI-Enhanced VFX: Improving Efficiency and Creativity
The greatest advantage of AI in VFX lies in its ability to balance efficiency and artistry.
AI assists creators in generating realistic textures, predicting visual continuity, and even enhancing facial animation through motion learning. By minimizing manual labor, production teams can deliver cinematic-quality visuals on tighter timelines and budgets.
1. Speed and Efficiency
By automating labor-intensive tasks, AI allows production teams to meet tight deadlines without sacrificing quality—ultimately lowering costs and boosting output volume.
2. Consistency Across Scenes
AI algorithms maintain consistent color schemes, textures, or special effects throughout a project. This ensures brand or cinematic identity remains cohesive, even if footage comes from multiple cameras or locations.
3. Unlocking Creative Possibilities
With routine edits automated, artists have more bandwidth for ideation and experimentation—potentially leading to more innovative visual storytelling.
4. Scalability for Smaller Teams
Previously, high-end VFX required large, specialized teams. Now, smaller crews or even solo creators can compete on visual quality by leveraging user-friendly AI tools.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Pitfalls
As AI VFX becomes more advanced, so do the ethical challenges that come with it. From deepfake misuse to concerns about artistic authenticity, creators and brands must navigate these issues carefully to maintain audience trust and professional integrity. Below are some of the key concerns shaping the ethical landscape of AI in visual effects.
Deepfake Misuse
While AI-driven facial replacement can enhance storytelling, it also raises concerns about creating deceptive or manipulative content. Brands must disclose any face-swapping or synthetic media usage to maintain trust.
Copyright and IP Issues
Style transfer and content-aware fills often rely on large datasets. If these datasets aren’t properly licensed or contain copyrighted material, creators risk legal repercussions.
Uncanny Valley Effects
If AI-generated visual elements aren’t polished, they may look off or “creepy,” breaking audience immersion. Skilled artists still need to refine outputs to ensure a natural, coherent style.
Loss of Human Craftsmanship
Some worry that automated VFX will diminish the artistry once honed by skilled compositors and colorists. The industry must strike a balance between preserving human craftsmanship and embracing technological efficiency.
Explore the broader ethical challenges of AI in marketing in Ethics in AI Marketing: Balancing Personalization and Privacy.

Best Practices for Implementation
Start with Clear Objectives
Define what you want to achieve—time savings, enhanced realism, a specific visual style—so you can select the right AI tools and techniques.
Vet Your Datasets
Ensure any reference material or training data is legally and ethically sourced. Document your data pipeline to prove compliance with copyright laws.
Maintain a Human Touch
AI can accelerate workflows, but human creativity and quality control remain indispensable. Continually review and refine AI outputs to align with your project’s vision.
Disclose Synthetic or Altered Footage
If your project involves significant AI-driven alterations, consider disclosing it—especially if it features real people—to preserve audience trust and avoid misinterpretation.
Test, Iterate, and Document
Just like any technical process, AI-VFX integration requires trial and error. Keep notes on successful techniques, pitfalls, or resource needs so future projects can build on gained knowledge.
For more on blending human ingenuity with AI workflows, see Generating High-Impact Content with AI: Tips, Tools, and Best Practices.
The Future of AI VFX in the Industry
As AI continues to evolve, its role in VFX will expand far beyond automation.
Expect to see AI-driven simulations, real-time rendering, and predictive modeling becoming standard tools in production houses. This integration will not only enhance storytelling but also empower smaller studios to compete with major industry players.
Real-Time VFX
As hardware accelerators become more powerful, we can expect real-time AI-driven effects for live broadcasts, virtual events, and interactive experiences—lowering latency to near-instantaneous rendering.
Hyper-Realistic Avatars
Advances in motion capture and deep learning could result in photorealistic digital doubles, opening up new possibilities in gaming, virtual influencers, and remote collaboration.
Collaborative AI Systems
Teams might employ multiple AI models, each specialized in color grading, animation, or face mapping, working together under a unified pipeline. This modular approach could further streamline production.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Governments and professional bodies may introduce guidelines or labeling requirements for AI-altered media, ensuring transparency in journalism, advertising, and entertainment.

Conclusion
AI-enhanced visual effectsstand poised to redefine how videos are conceptualized and crafted. By automating tedious tasks, these technologies offer creators more time to focus on storytelling and innovation. Yet alongside the benefits come ethical and technical challenges—from potential deepfake misuse to IP concerns—that must be navigated carefully. The key lies in adopting AI as a collaborative partner rather than a total replacement for human artistry. With responsible implementation and ongoing refinement, brands and filmmakers can harness AI-driven VFX to produce content that’s both visually stunning and ethically sound.